Depression affects millions of people around the world. In the United States alone, the prevalence of depression has been on the rise in recent years. From 2005 to 2019, the percentage of adults aged 26 to 49 who had experienced a major depressive episode (MDE) in the past year increased from 7.6 percent (equivalent to 7.5 million people) to 8.9 percent (equivalent to 8.9 million people).
Moreover, the percentage of individuals with severe impairment due to a past year’s MDE also increased from 4.8 percent (or 4.8 million people) in 2009 to 6.1 percent (or 6.1 million people) in 2019.
By understanding the signs and symptoms of depression, we can work towards creating more effective treatments and support systems for struggling people.
In this article, we will explore how depression manifests differently in men and women and offer some tips for seeking mental health support.
Common Signs of Depression in Women vs. Men
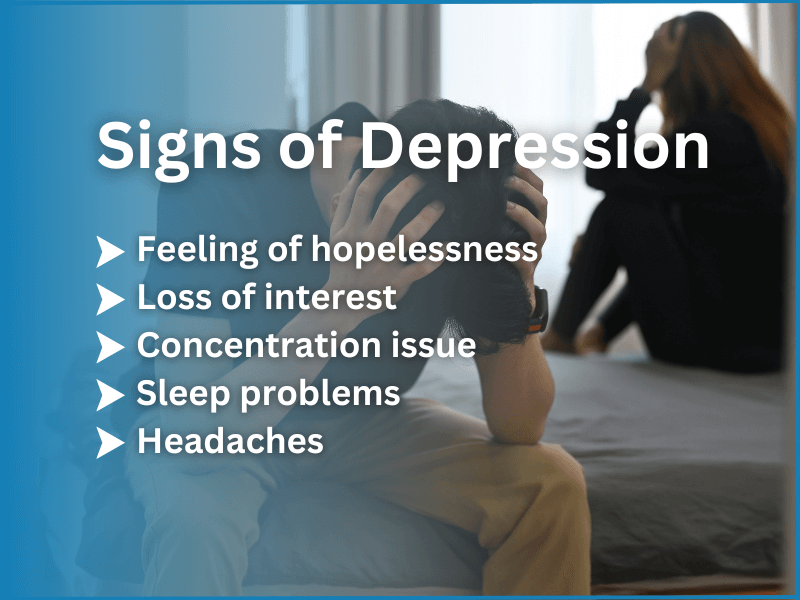
While occasional sadness or being down don’t necessarily indicate depression, it’s important to understand that depression is a complex mood disorder that goes beyond temporary negative emotions due to life events such as a breakup or a difficult week. Major depressive disorder involves a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s daily functioning and requires professional evaluation and treatment.
Depression can affect anyone, but it often manifests differently between men and women. Nevertheless, these are symptoms of depression in both genders:
Feelings of Hopelessness
People with depression may feel like nothing will ever improve or that they can’t escape the endless cycle of sadness.
Hopelessness can lead to thoughts of giving up on goals and dreams, withdrawing from once enjoyable activities, or feeling like it’s impossible to escape their current situation.
Loss of Interest in Daily Activities
Another sign of depression is losing interest in activities that once brought joy. For example, people with depression may lose interest in hobbies, favorite pastimes, or spending time with friends and family. As a result, even getting out of bed can feel like an impossible task.
Concentration Issues
Depression can make it difficult to focus on anything, from simple tasks to complex problem-solving. In addition, people with depression may struggle with concentration due to low energy levels and lack of motivation caused by negative thoughts associated with sadness.
Sleep Problems
People with depression may experience symptoms that affect their sleep, leaving them exhausted and irritable during the day.
Unfortunately, this can snowball into other problems, such as the following:
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): CFS is a complex and debilitating medical condition characterized by extreme fatigue that any underlying medical condition cannot explain.
- Difficulty regulating emotions: Lack of sleep can make it harder for people to control their emotions, leading to mood swings and heightened sensitivity to stressors.
- Relationship problems: Irritability and fatigue can strain relationships with friends and family, leading to social isolation and loneliness.
- Worsening of depression symptoms: The lack of quality sleep can also exacerbate existing depression symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle of negative emotions and poor sleep.
- Impaired work performance: People with depression who experience sleep-related issues may struggle to perform well at work or school, leading to further stress and negative consequences in their professional lives.
Headaches
Headaches are a common symptom of major depression and can vary from mild, dull aches to intense, sharp pain.
Depression-related headaches may be worse in the morning or during times of stress and could last for several hours or days. However, it’s important to note that headaches can also be a side effect of medication used to treat depression.
Anxiety and Depression
Major or clinical depression is a complex mental illness that can manifest in a variety of ways. In addition to the common symptoms we discussed earlier, it’s important to note that depression and anxiety are often linked. Anxiety can be a possible symptom of depression, or it can also trigger depression.
A significant number of individuals experience both depression and anxiety, although these are distinct conditions that share some similar symptoms, such as:
- Difficulty sleeping
- Nervousness
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
If you are experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor to determine whether you are dealing with anxiety, depression, or both.
What Depression Looks Like in Men

Depression is a treatable condition; men can overcome it with proper support and treatment and lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Unfortunately, men are more likely not to acknowledge their depression or even recognize it, leading to a delay in seeking help.
Men need to recognize these signs of depression in men and seek help when needed:
Substance Use and Abuse
Men are more likely to turn to drugs and alcohol when depressed. Unfortunately, this behavior can create a vicious cycle of increased depression, further substance abuse, and other challenging behaviors that will need intervention and treatment to stop.
Moreover, substance use is generally seen as more socially acceptable among men than women, increasing its prevalence.
Violence
Violent behaviors in men can be directed towards themselves or someone else and should not be taken lightly.
Men may also have difficulty discussing their feelings openly and tend to suppress them, which can lead to explosive outbursts and aggressive behavior.
Risky Behavior
Depression in men can also manifest in risk-taking behavior. For example, men may be more prone to:
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Men may also engage in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as a coping mechanism for their depression. Men with depression who also have ADHD may have a harder time seeking help and adhering to treatment plans, making it crucial to address both conditions in a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Reckless driving: Men with depression may engage in dangerous driving behaviors, such as speeding, driving under the influence, or engaging in road rage.
- Gambling: Men may be more likely to engage in gambling to escape their depression symptoms or cope with negative emotions.
- Thrill-seeking activities: Men may engage in risky activities, such as extreme sports or dangerous hobbies, to feel excitement or control.
- Workaholism: Men with depression may throw themselves into work to distract themselves from their negative emotions or feelings of hopelessness.
These behaviors lead to accidents, financial ruin, and other dangerous situations for themselves and others.
What Depression Looks Like in Women

Women with depression may experience a range of mood changes, such as persistent sadness, feelings of hopelessness, irritability, and anxiety. Additionally, they may experience other symptoms, such as difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and fatigue, as well as the following:
Physical Manifestations
Depression can have physical manifestations, and women may experience changes in their weight, which could be either weight gain or weight loss. Weight changes can lead to further complications such as disrupted sleep, body image issues, and other health concerns. It’s essential to recognize these symptoms and changes in women and seek appropriate help and support.
Feelings of Worthlessness
Depression in women is more likely to lead to a deep sense of worthlessness and guilt, especially regarding their role in relationships and their ability to provide for their families.
Women may beat themselves up over things that have gone wrong in the past or feel like they don’t measure up compared to other women around them. This can further exacerbate depression symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle of negative self-talk and low mood.
Self-Criticism
Women are more likely to blame themselves for difficult situations, leading to feelings of worthlessness and guilt.
Common depression signs and symptoms include thoughts like, “I’m a failure” or “This is all my fault.” This thinking leaves them feeling helpless and hopeless about their ability to change their lives.
Appetite Changes
Women may eat more or less than usual, and their weight may fluctuate. In addition, some women may struggle to maintain a healthy relationship with food, turning to food for comfort when feeling down or anxious.
Depression and diet can have a complicated relationship, so seeking help from a healthcare provider or mental health professional is vital if your eating habits are causing distress.
This behavior can exacerbate depression by leading to unhealthy habits and feelings of guilt and shame. It’s tricky to distinguish between eating due to depression and a healthy appetite.
Seeking Mental Health Support
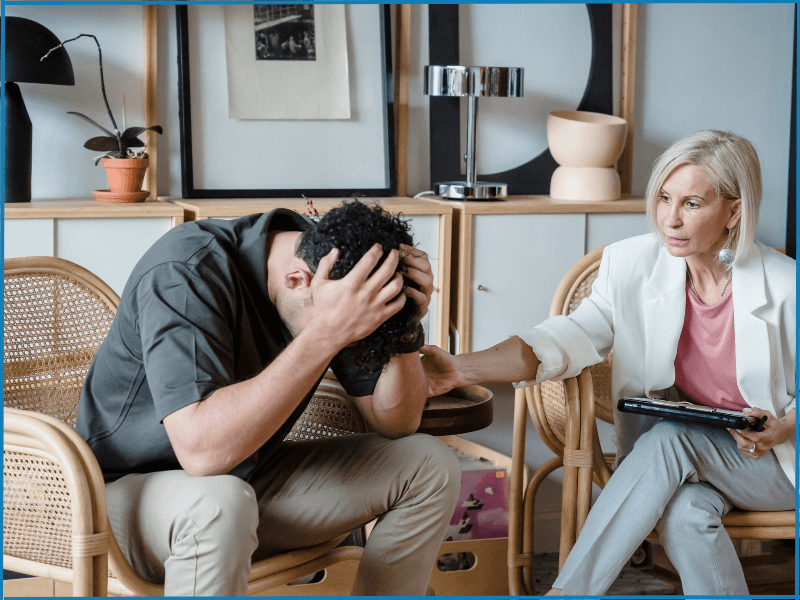

Depression can be a debilitating condition that affects many aspects of a person’s life. Therefore, seeking professional help is essential if you suspect you or a loved one may struggle with depression.
Remember that seeking help for depression is a sign of strength, not weakness. With the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage depression and lead a healthy, fulfilling life.
Here are some tips for seeking mental health support:
Talk to Your Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider can help you get started with a diagnosis and treatment plan for depression. In addition, they may refer you to a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or therapist, who can provide additional support.
Seek Out Support Groups
Many support groups exist for people struggling with depression. Support groups can offer a sense of community and understanding that can help manage symptoms and cope with the condition.
Find a Mental Health Professional
Mental health professionals, such as therapists, psychologists, and psychiatrists are trained to help individuals with various mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder. They can offer a range of treatment options, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, or a combination of both.
- CBT is a type of talk therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety and depression.
- Medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can also help manage anxiety disorders.
It’s important to note that seeking help from a mental health professional doesn’t mean you’ll automatically be prescribed medication.
Your mental health professional will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and goals. This may include exploring various treatment options, such as therapy or lifestyle changes, before considering medication.
Overall, if you’re experiencing symptoms of an anxiety disorder or any other mental health condition, seeking help from a mental health professional can be an essential step in managing your symptoms and improving your overall well-being.
Make Lifestyle Changes
In addition to professional treatment, you can also make lifestyle changes to help manage depression symptoms. These include exercise, healthy eating, stress reduction techniques, and social support.
Final Thoughts: Seeking Help for Depression
Depression can affect anyone, regardless of gender. Therefore, it’s important to recognize the signs of depression and seek help when needed. In addition, seeking professional support is crucial in managing depression symptoms and improving overall well-being.
If you or a loved one is struggling with depression, consider seeking treatment at a residential treatment center for depression. These facilities offer specialized care in a supportive and structured environment, providing individuals with the tools to manage their depression and lead fulfilling lives.
To learn more about the best inpatient depression treatment centers in the U.S., check out this article.
